筆記
從一開始的 printf 就讓人轉不過來,大致上,閱讀到中間(C 部分結束)時,幾乎答案都跟候選人一相同。
那~~~會不會碰到這些問題,我想大概機率很低吧!個人會選擇些 walk around 的方式,一定有 初始值 & 回傳值等等。
PS: a + a++ 應該躲不掉。
至於問我懂不懂 C 的話,我想我應該會肯定的回答 我懂我目前應該知道的部分 這樣的回答吧!
printf 1 2 3 4 int main () int a = 42 ; printf ("%d\n" ,a); }
C2 回答:
回傳值通常會從 register 回傳,所以會回傳 printf 的結果 3
int main(void) 才是不收參數的寫法最後要多空一行(好像很常看到,有些 IDE 也會幫忙補)
變數 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 int a;static int b;void func () int c; static int d; c++; printf (%d ,c); }
C2 回答:
a = 0,linker visibilityb = 0,local to this compilation unit not visible to linkerc = 0,理論上是 garbage,但沒最佳化的話通常會拿到同一塊記憶體,所以有可能印出 1 2 3d = 0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 void foo (void ) int a; printf ("%d\n" ,a); } void bar (void ) int a = 42 ; } int main (void ) bar(); foo(); }
C2 回答:
foo 視為 inline function
execution stack
activation frame
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 void foo (void ) int a = 41 ; a = a++; printf ("%d\n" ,a); } int main (void ) foo(); }
C2 回答:
can be 42 41 43 0 1099(why?)
sequence point
1 2 printf ("%d\n" , sizeof (int ));sizeof char * d;
C2 回答:
size_t 應用 %zu
in 64-bit machine 32-bit compatibility char * d 佔 8
Memory Model static storage 1 2 3 4 int * immortal (void ) static int storage = 42 ; return &storage; }
automatic storage 1 2 3 4 int * zombie (void ) auto int storage = 42 ; return &storage; }
allocated storage 1 2 3 4 5 int * finite (void ) int * ptr = malloc (sizeof *ptr); *ptr = 42 ; return ptr; }
Register 37 個 Register
30 個 通用 Register
1 PC Program Counter
1 CPSR (Current Program Status Register)
5 SPSR (Saved Program Status Register)
SP Stack Point
LR Link Register
objdump
P101~P108 解釋了 caller(r0~r3) & callee(r4~r11) save & restore register 的過程
以及 call function 時,也會 save LR,以便 return 時讓 PC 跳回來
p142 ~ P143
149~151
Code optimization GCC
commom sub-expression elimination
dead code removal
induction variables & Strength reduction
loop unrolling
funciton inlining __inline
ARM
barrel shifter 5*x -> (x<<2) + x
count down loop
盡可能用 32 bit data type
如果沒有 side effect,可宣告成 pure func 以便最佳化 __pure
GDB GDB 對我來其實還不會太陌生,在 iOS debug 的時候通常會配合 IDE + LLDB 使用,
畢 LLDB 是 GDB like,有些指令還是不太一樣,所以還是自己弄個環境來完一下。
最後弄了 docker gdb_practice ,練習 通过 GDB 学习 C 语言 & Introduction to gdb
也玩了下遠端debug gdb server ,用 B container link A container 的方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 docker run -it \ --security-opt seccomp=unconfined \ --rm \ -v /path/to/build:/build \ -p 2222:2222 \ --name gdb_server \ quay.io/yume190/gdb_practice docker run -it \ --security-opt seccomp=unconfined\ --rm \ -v /path/to/build:/build \ --link gdb_server:gdb_server \ --name gdb_client \ quay.io/yume190/gdb_practice
透過 GDB Rocks! 了解 gdb 的特殊技
attach process
Jump PC
Core dump(查了資料但還沒實際玩過)
插曲:
在 Mac 上用 gcc compile 過後 gdb run 不起來
以及在 container run gdbserver,並用 Mac 當 gdb client 嘗試 remote debug 也不太順利
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 gdb binary.o r # run b # breakpoint next step stepi disas info breakpoints info frame info stack info locals display/{format} x examine p print wa watch ptype # format = {數量}{format}{size} # format x hexadecimal o octal d decimal u unsigned decimal t binary f float a address i instruction c char s string # size b byte h halfword w word g giant 8 bytes
系統程式 感覺讀的順序應該是:
from Source to Binary: How GNU Toolchain Works How A Compiler Works: GNU Toolchain The Internals of “Hello World” Program
from Source to Binary: How GNU Toolchain Works 可以看到整個 toolchain 大致在做什麼
How A Compiler Works: GNU Toolchain 看到 compiler 在不同階段可以最佳化的介紹
但內容部分有不少跟 from Source to Binary: How GNU Toolchain Works 有些重複
比較閃到我眼睛的應該是:
IPO(Inter-Procedural Optimization) -> WPO(Whole-Program Optimization)
LLVM 一直排在待看列表中
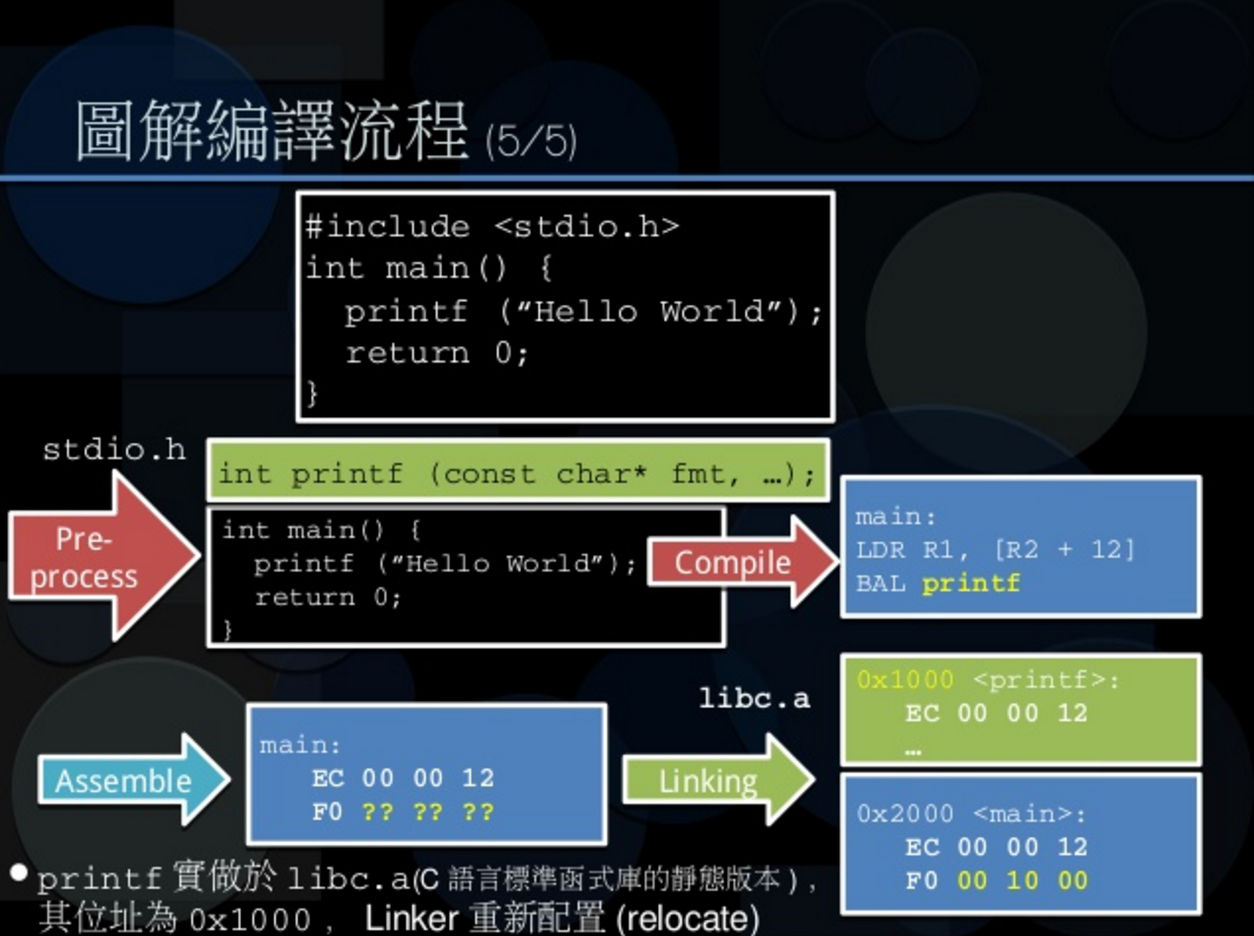
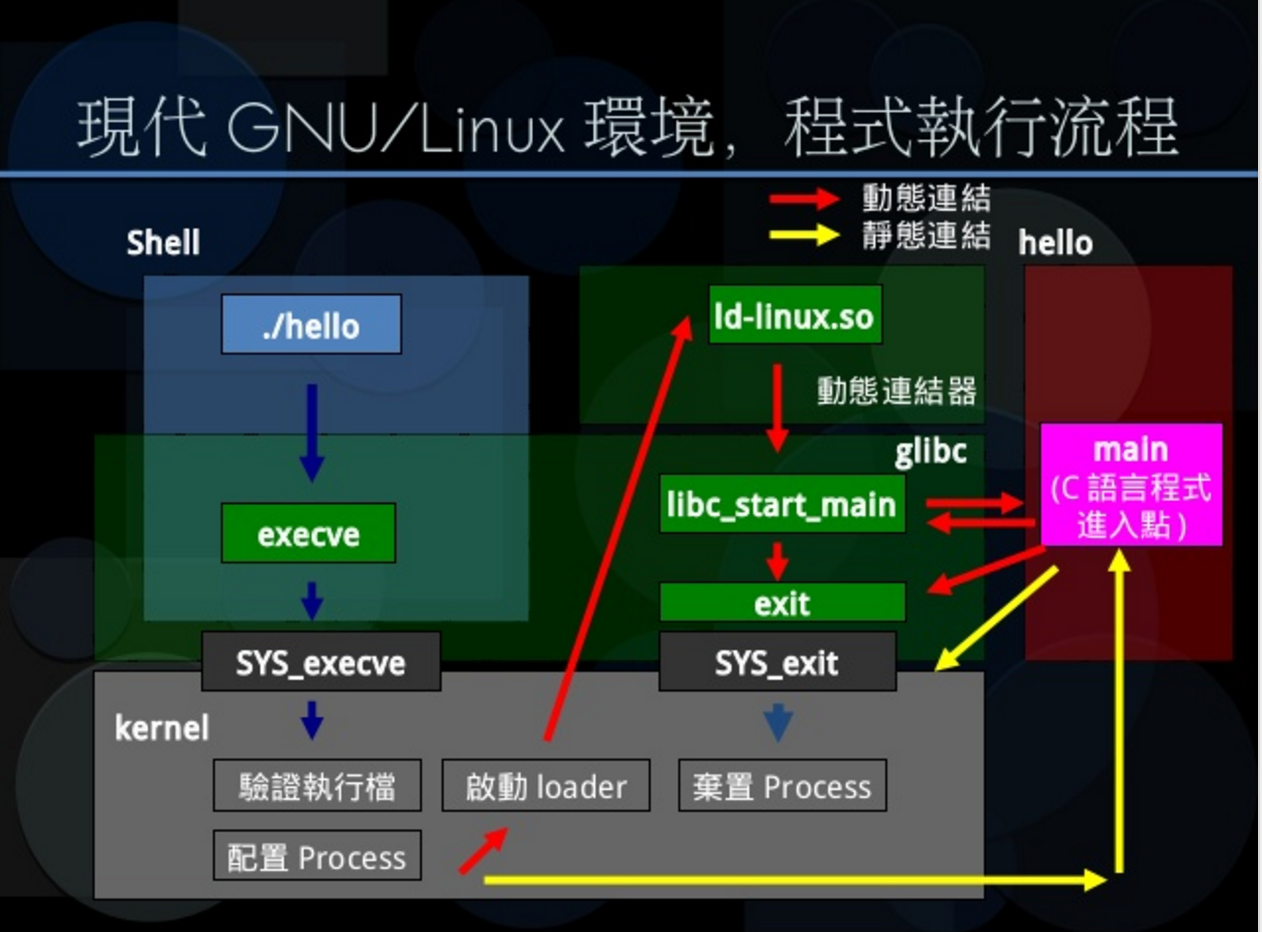
The Internals of “Hello World” Program
跟著實際操作後,可以了解從 .o 到可執行檔,ld 進行 彙整 Relocation Symbol Resolve 的結果
並且了解 ELF 有各個區塊,並且能過既有工具檢視它(nm readelf objdump)
P3~P7
理解優化五大階段 編譯階段
連結階段
載入階段
三大法寶
GCC(Compiler)
Binutils(Assembler, Linker)
libc(C Libary, eglibc/bionic)
Compile 原始碼 -> 字彙分析 (正規語言) -> 語法分析 (Context-Free Grammar) -> 語法樹 -> 語意分析 (Type Checking ..etc) -> 中間語言 -> 優化 -> 目標語言
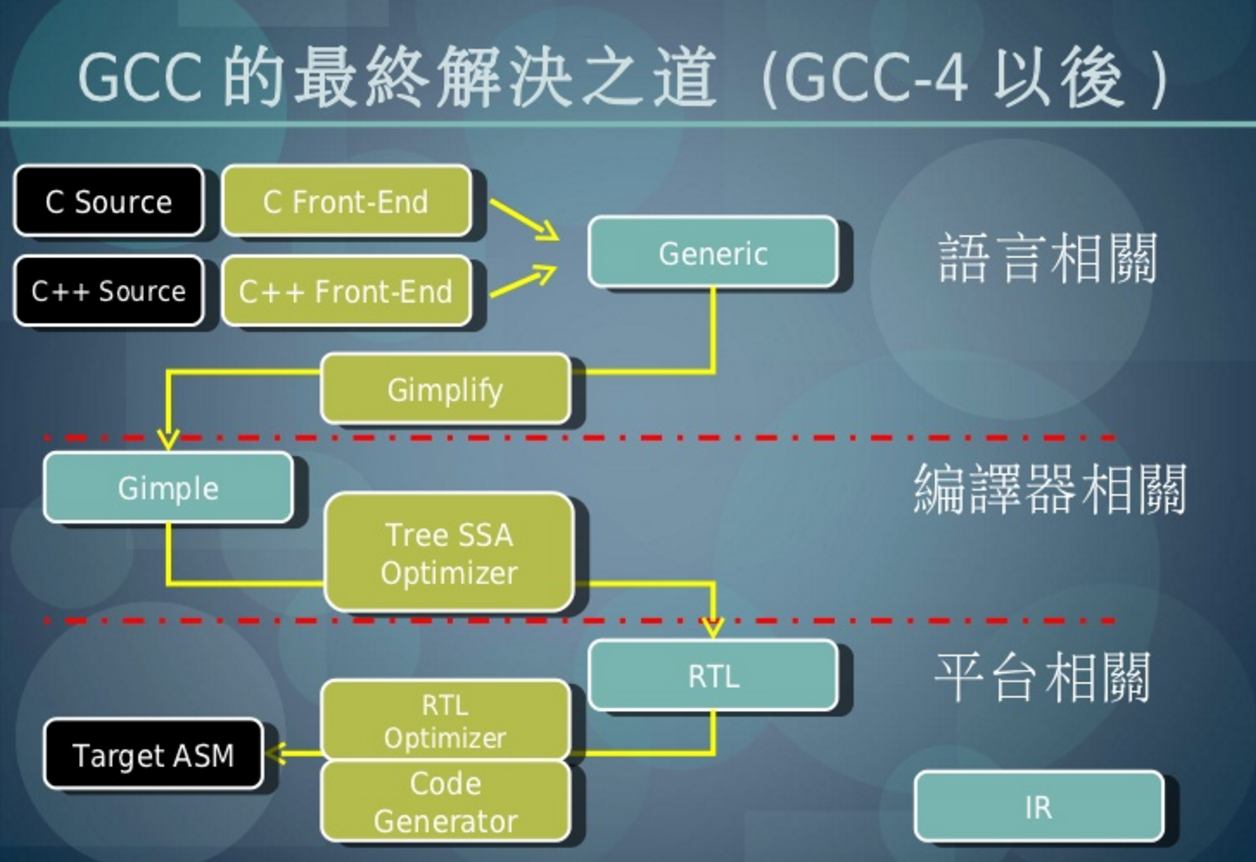
語言相關
編譯器相關
平台相關
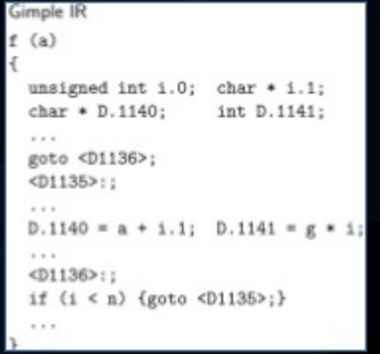
Generic -> Gimplify ->
Gimple -> Tree SSA Optimizer ->
RTL -> RTL Optimizer/Code Generator -> target
GCC IR:
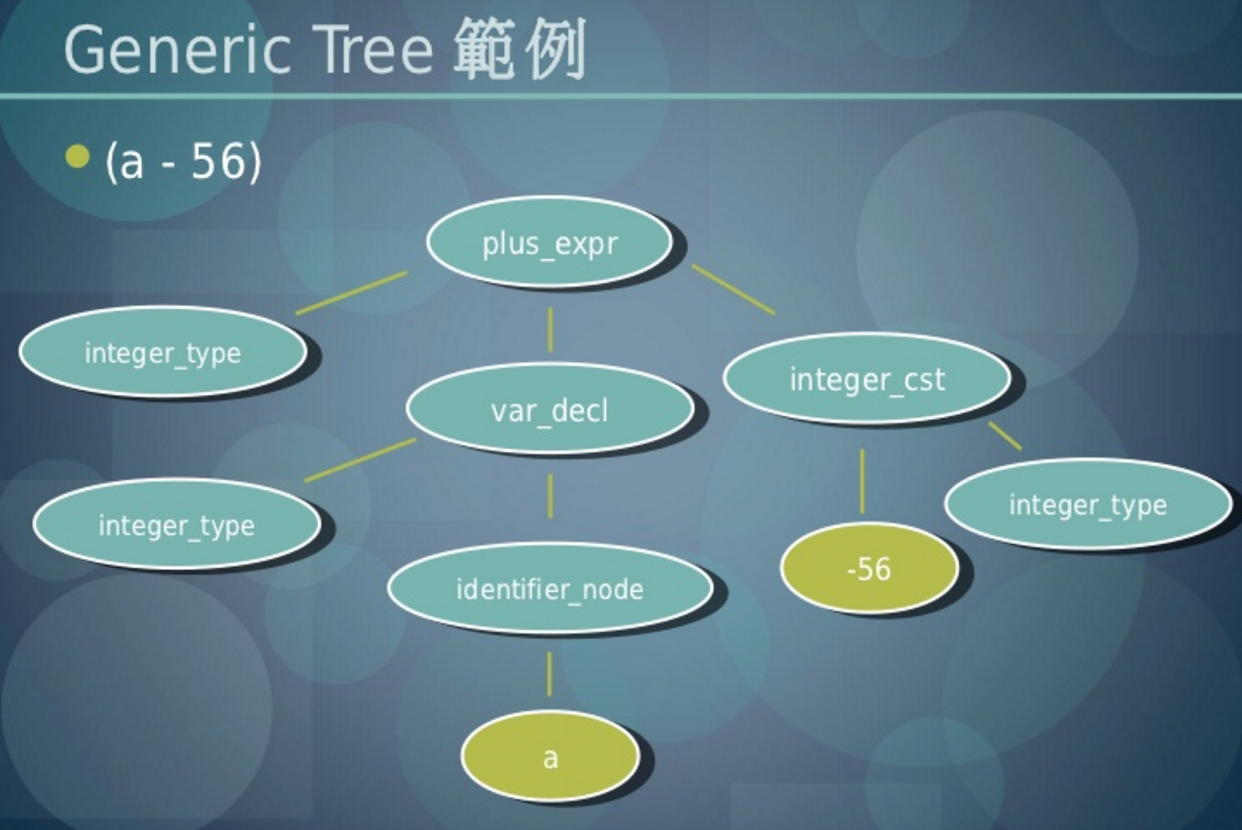
High Level: Generic(Syntax Tree Style IR)
Middle Level: Gimple(Tree Style IR, SSA Form)
Low Level: RTL(List Style IR, Register Based)
Static Single Assignment 每個變數只會被 assign 一次
每 assign 一次 Version Number 增加
使用 Φ function
Register Transfer Language
Use Virtual Register(無限 Register)
Intruction scheduling
peephole optimization
組譯
連結
把所有目的檔彙整成執行檔
Symbol Resolve
處理 Relocation Type
1 2 3 4 gcc hello.c -o hello.o gcc hello.c -S -o hello.s gcc hello.s -o hello.o gcc hello.c -o hello.o -v --save-temps # 動作解析
How A Compiler Works: GNU Toolchain
code motion(程式碼搬移)
loop invariant : 迴圈內有些計算,不管幾次都是一樣結果
data flow analysis : 分析指令有無相依,無相依有機會調換位置
code motion & Pointer Aliasing
變成 0 的魔法 : P42~54
深入淺出 Compilation Unit P69
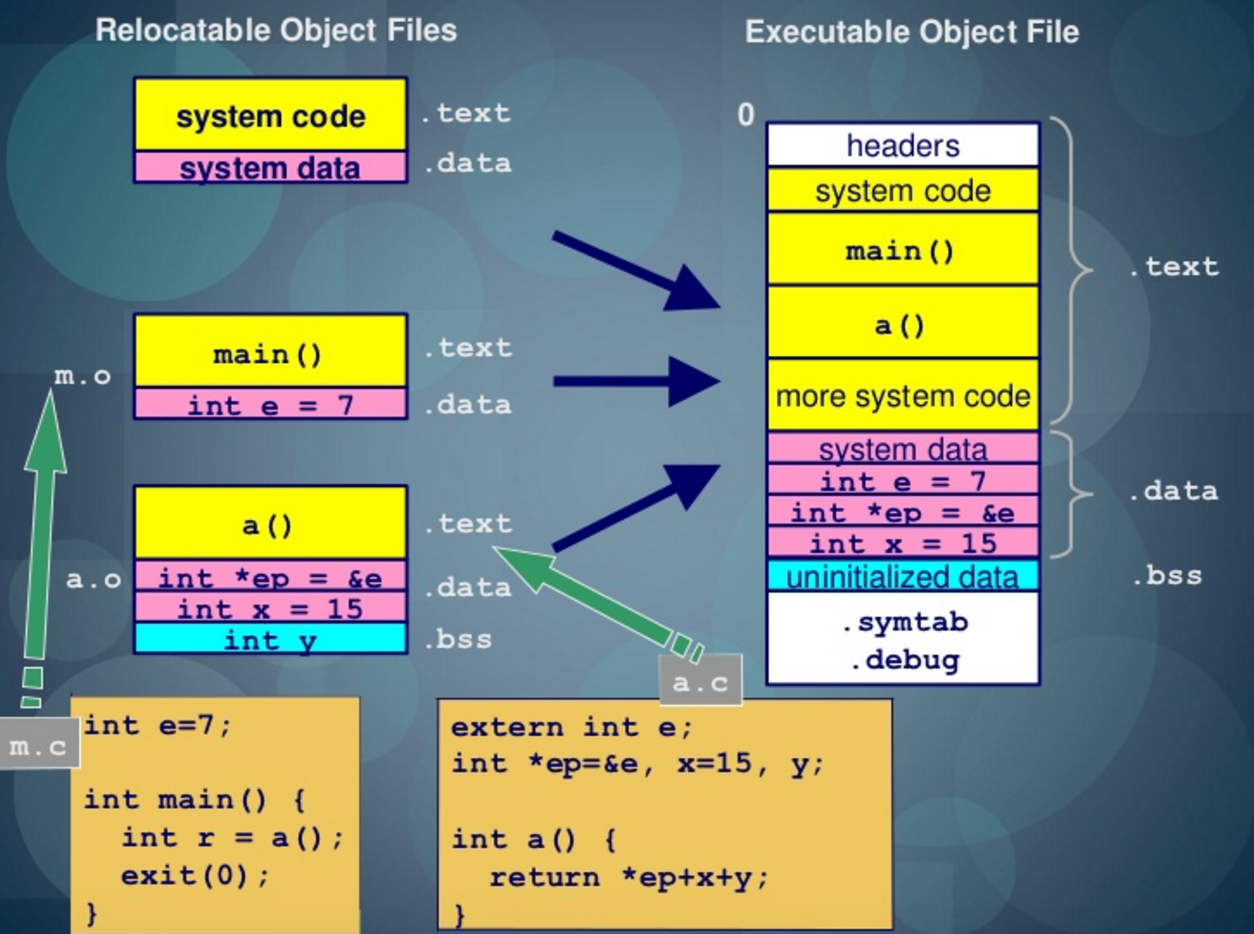
PS:如果確定沒別的檔案會使用這個 func or var,請宣告成 static foo.c 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 #include "bar.h" int foo = 3 ;int main () foo = 8 ; bar(&foo); return 0 ; }
bar.c 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 #include <stdlib.h> void bar (int *val) *val = 11 ; val = NULL ; *val = 17 ; }
1 2 gcc -c foo.c bar.c ld foo.o bar.o -e main foobar
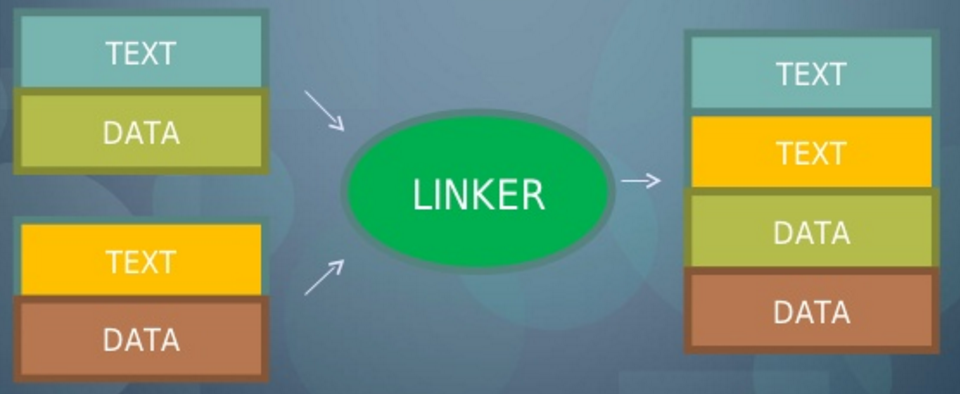
linker 彙整
foo text 1f
bar text 26
foobar text 1f + 26 = 45
objdump -h foo.o 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 foo.o: file format elf64-x86-64 Sections: Idx Name Size VMA LMA File off Algn 0 .text 0000001f 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000040 2**0 CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, RELOC, READONLY, CODE 1 .data 00000004 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000060 2**2 CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, DATA 2 .bss 00000000 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000064 2**0 ALLOC 3 .comment 0000001e 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000064 2**0 CONTENTS, READONLY 4 .note.GNU-stack 00000000 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000082 2**0 CONTENTS, READONLY 5 .eh_frame 00000038 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000088 2**3 CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, RELOC, READONLY, DATA
objdump -h bar.o 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 bar.o: file format elf64-x86-64 Sections: Idx Name Size VMA LMA File off Algn 0 .text 00000026 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000040 2**0 CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, CODE 1 .data 00000000 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000066 2**0 CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, DATA 2 .bss 00000000 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000066 2**0 ALLOC 3 .comment 0000001e 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000066 2**0 CONTENTS, READONLY 4 .note.GNU-stack 00000000 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000084 2**0 CONTENTS, READONLY 5 .eh_frame 00000038 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 00000088 2**3 CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, RELOC, READONLY, DATA
objdump -h foobar 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 foobar: file format elf64-x86-64 Sections: Idx Name Size VMA LMA File off Algn 0 .text 00000045 00000000004000e8 00000000004000e8 000000e8 2**0 CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, CODE 1 .eh_frame 00000058 0000000000400130 0000000000400130 00000130 2**3 CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA 2 .data 00000004 0000000000600188 0000000000600188 00000188 2**2 CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, DATA 3 .comment 0000001d 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0000018c 2**0 CONTENTS, READONLY
Relocation foo 1 13: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 18 <main+0x18>
foobar 1 2 4000fb: e8 07 00 00 00 callq 400107 <bar> 0000000000400107 <bar>:
foo.rela.text 1 000000000014 000a00000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 bar - 4
可以從 foo.rela.text 看到 foo 位置 0x14 會被 Relocation,
也就是 foo 的 e8 00 00 00 00
被 Relocation 為 e8 07 00 00 00 )
也就是 linker 彙整完畢後, bar function 所在地 0x400107
Relocation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 objdump -d foo.o foo.o: file format elf64-x86-64 Disassembly of section .text: 0000000000000000 <main>: 0: 55 push %rbp 1: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp 4: c7 05 00 00 00 00 08 movl $0x8 ,0x0(%rip) b: 00 00 00 e: bf 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0 ,%edi 13: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 18 <main+0x18> 18: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0 ,%eax 1d: 5d pop %rbp 1e: c3 retq objdump -d foobar foobar: file format elf64-x86-64 Disassembly of section .text: 00000000004000e8 <main>: 4000e8: 55 push %rbp 4000e9: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp 4000ec: c7 05 92 00 20 00 08 movl $0x8 ,0x200092(%rip) 4000f3: 00 00 00 4000f6: bf 88 01 60 00 mov $0x600188 ,%edi 4000fb: e8 07 00 00 00 callq 400107 <bar> 400100: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0 ,%eax 400105: 5d pop %rbp 400106: c3 retq 0000000000400107 <bar>: readelf -r foo.o Relocation section '.rela.text' at offset 0x240 contains 3 entries: Offset Info Type Sym. Value Sym. Name + Addend 000000000006 000800000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 foo - 8 00000000000f 00080000000a R_X86_64_32 0000000000000000 foo + 0 000000000014 000a00000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 bar - 4 Relocation section '.rela.eh_frame' at offset 0x288 contains 1 entries: Offset Info Type Sym. Value Sym. Name + Addend 000000000020 000200000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 .text + 0
Symbol Resolution 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 readelf -s foo.o Symbol table '.symtab' contains 11 entries: Num: Value Size Type Bind Vis Ndx Name 10: 0000000000000000 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT UND bar ld foo.o -e main -o foobar foo.o: In function `main': foo.c:(.text+0x14): undefined reference to `bar' readelf -s foobar Symbol table '.symtab' contains 13 entries: Num: Value Size Type Bind Vis Ndx Name 12: 0000000000400107 38 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 1 bar
Segment 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 readelf -l foobar Elf file type is EXEC (Executable file) Entry point 0x4000e8 There are 3 program headers, starting at offset 64 Program Headers: Type Offset VirtAddr PhysAddr FileSiz MemSiz Flags Align LOAD 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000400000 0x0000000000400000 0x0000000000000188 0x0000000000000188 R E 200000 LOAD 0x0000000000000188 0x0000000000600188 0x0000000000600188 0x0000000000000004 0x0000000000000004 RW 200000 GNU_STACK 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 RW 10 Section to Segment mapping: Segment Sections... 00 .text .eh_frame 01 .data 02
Dynamic Link Load Time Relocation -shared
Position-Indepent Code(PIC) -fPIC
Inter-module funciton call -> PLT -> GOT GOT(Global Offset Table)